The Legal and Regulatory Framework for Online Gambling in the United States

Gambling has been a popular pastime for many Americans, but online gambling has become increasingly prevalent with the advent of the internet. However, the legal and regulatory framework for online gambling in the United States is complex and constantly evolving, with a patchwork of federal and state laws and regulations that can be difficult to navigate. This article will explore the legal and regulatory framework for online gambling in the United States, including the relevant federal and state laws and regulations.
Federal Laws and Regulations
The primary federal law governing online gambling in the United States is the Wire Act of 1961. This law prohibits using wire communications facilities to transmit bets or wagers or information assisting in placing bets or wagers on any sporting event or contest. The Wire Act has traditionally been interpreted to apply only to sports betting and not to other forms of online gambling, such as casino games or poker.
While state laws and regulations are a crucial component of the legal framework for online gambling, federal laws and regulations also play an essential role.
In 2006, the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act (UIGEA) was passed, prohibiting financial institutions from processing payments related to illegal online gambling. The UIGEA does not make online gambling illegal. Still, it has significantly impacted the online gambling industry by making it more difficult for players to deposit and withdraw funds.
In 2011, the Department of Justice (DOJ) issued a legal opinion stating that the Wire Act applied only to sports betting, not other forms of online gambling. However, in 2018, the DOJ issued a new legal opinion, reversing its previous position and stating that the Wire Act applies to all forms of online gambling.
This new legal opinion has caused significant concern within the online gambling industry. It could be used to bring criminal charges against operators and players in states where online gambling is legal. However, some legal experts have argued that the new legal opinion is flawed and may face legal challenges in the courts.
In addition to the Wire Act, the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act (UIGEA) also significantly impacts the online gambling industry. The UIGEA prohibits financial institutions from processing payments related to illegal online gambling, making it more difficult for players to deposit and withdraw funds from online gambling sites.
However, the UIGEA does not itself make online gambling illegal, and there are ways for players to participate in online gambling activities legally. For example, players in states where online gambling is legal can play on licensed and regulated platforms and use payment methods accepted by those platforms.
State Laws and Regulations
In addition to federal laws and regulations, online gambling is subject to state laws and regulations. In states where online gambling is legal, operators must obtain a license from the state regulatory agency to offer their services. These licenses typically come with various requirements, such as background checks on operators, age and location verification for players, and responsible gambling measures.
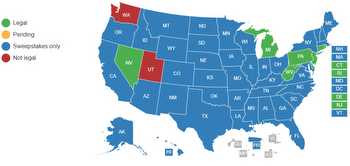
Some states have explicitly banned online gambling. For example, Utah and Hawaii have passed legislation prohibiting all forms of gambling, including online gambling. Other states, such as Washington, have taken a more aggressive approach to enforcement, with some players facing criminal charges for participating in online gambling activities.
However, many states are beginning to recognize the potential benefits of legalizing and regulating online gambling. In addition to generating tax revenue for the state, legalizing online gambling can also help to protect players by ensuring that they are playing on a fair and secure platform.
States that have legalized online gambling typically require operators to obtain a license from the state regulatory agency. These licenses usually come with various requirements, such as background checks on operators, age and location verification for players, and responsible gambling measures.
For example, online gambling operators in New Jersey must be licensed by the Division of Gaming Enforcement (DGE). The DGE has strict requirements for operators, including background checks on key personnel, technical audits of the online platform, and ongoing monitoring of player activity to detect potential problem gambling behaviors.
Similarly, online gambling operators in Pennsylvania must be licensed by the Pennsylvania Gaming Control Board (PGCB). The PGCB requires operators to implement various responsible gambling measures, including player self-exclusion options, limits on deposit amounts, and mandatory responsible gambling training for employees.
Challenges and Future Developments
One of the biggest challenges facing the online gambling industry in the United States is the lack of uniformity in laws and regulations across different states. This can confuse operators and players alike, making it difficult for the industry to grow and thrive.
However, there are also some positive developments on the horizon. In 2018, the Supreme Court struck down the Professional and Amateur Sports Protection Act (PASPA), which had effectively banned sports betting in most states. Since then, several states have legalized sports betting, and more are expected to follow.
Conclusion
The legal and regulatory framework for online gambling in the United States is complex and constantly evolving. While federal laws such as the Wire Act and UIGEA set some broad parameters for online gambling, it is mainly up to individual states to decide whether to legalize and regulate the industry. As the industry continues to grow and develop, we will likely see further changes to the legal and regulatory landscape in the years to come.