How has online casinos have evolved in the United States?

(STACKER) For years, casinos were physical spaces gamblers went to for a night on the town or a fun group outing with friends. But that’s all changed over the past 30 years, thanks to changes in technology and laws. Over the past several decades, online casinos have rapidly risen in popularity in the United States. The global market for online gambling is now expected to reach $172 billion by 2030, with millions of players gambling on various platforms.
To look at how and why, it’s helpful to consider a few key factors. First, the rise of internet technology in the late 1990s paved the way for the creation of the first online casinos, offering players a new way to experience their favorite games from the comfort of their own homes. Since then, the industry has grown in popularity. New technologies and legal developments further reshaped the landscape of online gambling in the country.
To understand just which moments were most important in the evolution of the online casino industry in the United States over the past few decades, The Game Day Casino compiled a list of the six most significant milestones in online gaming. These are a mix of technological, legal, and broader social trends, each leading to the others. These changes have opened up new opportunities for innovation and growth in the industry and are expected to continue shaping the future of online gambling in the years to come.
1990s: The rise of the internet
The rise of internet technology in the 1990s allowed for the creation of the first online casinos as it became possible to transmit data and graphics over the internet reliably and efficiently. The internet allowed for the development of software that could simulate the experience of playing traditional casino games, such as blackjack and slots, in a digital environment.
In 1994, the island country of Antigua and Barbuda passed the Free Trade and Processing Act, allowing individuals and businesses to set up online casinos. Hundreds of online casinos sprang up in the country, which led to the growth of its gambling industry. In its wake, more online gambling legislation materialized in Malta, New Jersey, and the Mohawk Territory of Kahnawake.
Online casinos also benefited from the growth of e-commerce, making it easier for players to make deposits and withdrawals online. The increasing popularity of home computers and high-speed internet connections provided a convenient and accessible platform for online gambling. Software company CryptoLogic made secure financial transactions possible online in 1995. A year later, InterCasino was the first online casino to use real money in wagers made on the internet, where there were just 15 such websites in existence. By 1997, online gambling sites increased to 200.
Early 2000s: The development of online payment systems
The growth of online payment systems, such as PayPal and other e-wallets, has revolutionized how online casinos operate. Previously, players were often hesitant to make deposits or withdrawals due to security concerns and the complexity of the payment process. The emergence of e-wallets has made the process much simpler and more secure, allowing players to make transactions with ease and confidence.
E-wallets also provide an additional layer of security. They act as a buffer between the player’s bank account or credit card and the online casino, reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access to sensitive financial information. This has helped to build trust and confidence in the online casino industry, making it more accessible and appealing to a wider audience.
2006: The Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act
The Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act of 2006 was a significant legal milestone in the history of online gambling. The law made it illegal for financial institutions to process transactions related to online gambling, effectively cutting off many online casinos from the U.S. market.
Before that, many more governments were trying to get a handle on online gambling. In 1999, there was the Internet Gambling Prohibition Act, which passed in the House of Representatives but failed in the Senate. In 2000, the Interactive Gambling Moratorium Act was passed by the Australian Federal Government, which made unlicensed online casinos operating before May 2000 illegal.
UIGEA had a major impact on the industry, forcing many operators to shut down or move their operations offshore. One of the major online poker rooms in the world, Party Gaming, left the U.S. market in response, and so did 888—both of which were publicly traded companies. The legislation also drove away e-wallet Neteller from U.S. shores as the Department of Justice froze U.S. player funds (which were returned in full after 1.5 years). Other players stayed in the U.S. market, however, and went on to take over the market Party Gaming left behind.
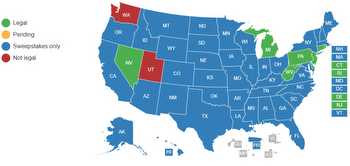
The law also paved the way for individual states—such as New Jersey in 2013—to legalize and regulate online gambling within their borders, leading to a patchwork of regulations and licensing requirements across the country.
Despite its impact on the industry, the UIGEA helped to bring greater clarity and transparency to the legal status of online gambling in the U.S. and made possible future developments in the industry.
2010s: The smartphone explosion
Mobile technology has had a significant impact on the online casino industry, as more and more players now access their favorite games from smartphones and tablets. This has led to the development of dedicated mobile apps and optimized mobile websites, allowing for a seamless and user-friendly gaming experience on the go.
Mobile technology continues to help online gambling make inroads, according to Acumen Research and Consulting. The gambling regulators they interviewed shared that most mobile gamblers are younger and often bet on sports. The firm predicts the fastest growth in online gambling will come from mobile gaming because of the increasing access to a smartphone and their corresponding gambling apps.
2011: Changes to the Wire Act
The Department of Justice’s reversal of its stance on the Wire Act in 2011 was a significant milestone for the online gambling industry. It cleared the way for states to legalize and regulate online poker and other forms of online gambling. The Wire Act, originally passed in 1961, had been interpreted to prohibit all forms of online gambling, but the DOJ’s reinterpretation in 2011 made it clear that the law only applied to sports betting. This led to a wave of legalization efforts nationwide, with states such as Nevada, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania leading the way.
The decision also paved the way for greater innovation and competition within the industry as more players and operators entered the market. However, the legal landscape remains complex, with a patchwork of state and federal laws governing online gambling and ongoing debates about the proper role of government regulation in the industry.
2020s: The growth of virtual reality and artificial intelligence
Technology continues to help push the envelope in what is possible, especially regarding player experience.
VR technology—where players use a headset to interact with a digital environment—allows players to step into a fully-realized digital casino environment, complete with realistic graphics, sound effects, and interactivity. On the other hand, artificial intelligence is a more subtle addition to the online gaming experience. By gathering player data, online casinos could offer a more personalized experience by suggesting similar games or genres, depending on the player’s tastes. It’s not unlike how Spotify or Netflix suggests new songs or titles for each user.
While AI and VR technology is still in the early stages of development, their potential impact on the online casino industry is significant. They are expected to be major areas of growth and innovation in the coming years.
This story originally appeared on The Game Day Casino and was produced and distributed in partnership with Stacker Studio.