The history of casinos and the law in New Zealand

The 1920s were a time when gambling was illegal in most places, save racetracks. That dynamic persisted until a legal reform in 1961 liberalized the sector. With the legalization of slot machines and the proliferation of live casinos around the country, New Zealand quickly became a major gaming destination. The Gambling Act of 2003 is the government’s last word on the subject.
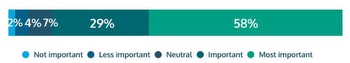
New Zealand, like its neighboring Antipodean country of Australia, has a strong love for casino games, particularly pokies. As a matter of fact, the statistics show that pokies generate 35% of total betting income, with other casino games coming in at a close second with 26%. The existence of no deposit bonuses in New Zealand could be the reason for the tremendous growth in the number of players.
NZ district introduces a new gambling harm policy
No more gaming facilities will be allowed, and the existing facilities will be prevented from relocating. Upon its approval at a meeting on June 23rd, the Gisborne District Council’s Gambling Venue Policy 2022 went into force. Its goals include the regulation of gaming expansion, the prevention and mitigation of gambling-related damage, and the promotion of public participation in gambling-related decision-making.
What does the New Zealand Act of 2003 entail?
By codifying the country’s gambling laws and providing a framework for the business in the age of the internet, the New Zealand Gambling Act of 2003 simplified the regulatory framework for the sector. The authorities behind its creation wanted to ensure that internet gambling would have no bad consequences, therefore they came up with this system.
The Gambling Act has been revised twice since it was first enacted, in 2005 and 2015, however the primary provisions remain unchanged. A previous iteration of the Gambling Act was titled the Responsible Gambling Bill (2002). This laid the groundwork for the present regulatory framework, which has been implemented to guarantee the greatest standards of service and security in the land-based and digital gaming industries.
Which other countries have regulated casinos?
In India, gaming is regulated under the Public Gambling Act, 1867. Goa and Sikkim are the only two states in India that have explicitly legalized gaming and betting, albeit these activities are nonetheless strictly regulated by state governments. Casino gambling is permitted in states like Goa.
The Gambling Act of 2005 made it lawful for those living in the United Kingdom to partake in gambling. The purpose of the present gambling legislation in the United Kingdom is to reduce the prevalence of underage gambling and to improve industry regulation for the protection of players.
China has also tightened its efforts in regulating online casinos. Although the number of licenses in Macau’s lucrative gambling center would not be limited under the new proposed rule, the period of new casino licenses would be halved and operations would be required to conform with China’s national security concerns.
Several governments have announced new regulations on betting companies in an attempt to reduce problem gambling.